2.8 KiB
Leetcode Path-Sum
2022-07-06 13:45
Algorithms:
#algorithm #DFS #recursion
Data structures:
#DS #binary_tree
Difficulty:
#coding_problem #difficulty-easy
Additional tags:
#leetcode
Revisions:
N/A
Related topics:
tag:#DFS
Links:
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Examples
Example 1:
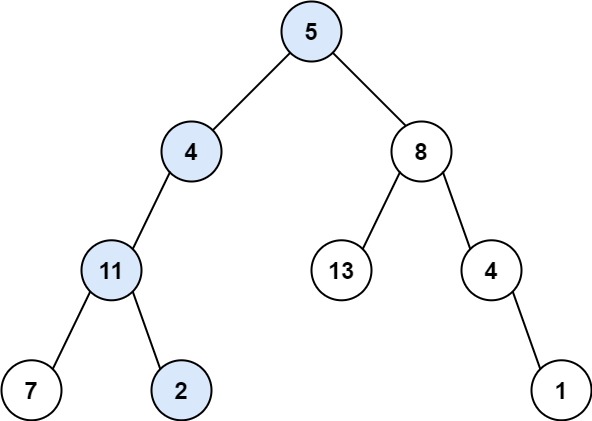
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 Output: true Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 Output: false Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree: (1 --> 2): The sum is 3. (1 --> 3): The sum is 4. There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0 Output: false Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Thoughts
[!summary] This is a #DFS recursion problem.
There are one thing to consider, return false when the tree is empty.
Simple DFS-like recursion problem.
Base cases:
- node is empty, return false
- node is leaf
- if the value is sum, return true
- else return false
Pseudo-code:
- Check for base-cases
- return check(left, sum - root->val) || check(right, sum - root->val)
[!tip] Why use OR By using OR operator, return true when there is at least one solution that matches.
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
// DFS In-order Recursion
// Base case: node does not exist
if (!root) {
return false;
}
int val = root->val;
// Base case: reached leaf
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (targetSum == val)
return true;
else
return false;
}
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - val);
}
};