3.6 KiB
3.6 KiB
Leetcode Remove-Linked-List-Elements
2022-06-15 21:50
Data structures:
#DS #linked_list
Difficulty:
#leetcode #coding_problem #difficulty-easy
Related topics:
tag:#linked_list
- Floyd's Cycle Finding Algorithm
- Leetcode Linked-List-Cycle
- Leetcode Merge-Two-Sorted-Lists
- Leetcode Remove-Duplicates-From-Sorted-List
- Leetcode Reverse-Linked-List
- Two pointers approach
Links:
Problem
Given the head of a linked list and an integer val, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has Node.val == val, and return the new head.
Examples
Example 1:
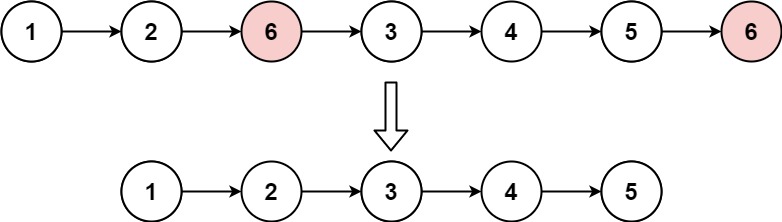
**Input:** head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 2:
**Input:** head = [], val = 1
**Output:** []
Example 3:
**Input:** head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
**Output:** []
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
Thoughts
Simple linked list operations, but remember to check for special cases:
- The pointer is null
Solution
Two pointers, O(n)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *removeElements(ListNode *head, int val) {
// O(n)
while (head != NULL && head->val == val) {
head = head->next;
}
ListNode *before = NULL;
ListNode *ptr = head;
ListNode *tmp;
while (ptr != NULL) {
if (ptr->val == val) {
if (before != NULL) {
before->next = ptr->next;
}
// delete ptr and change ptr to ptr->next
tmp = ptr->next;
delete ptr;
ptr = tmp;
} else {
before = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
These two are taken from discussions, and they are not memory safe. Recursive solution from the same guy:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *removeElements(ListNode *head, int val) {
// Base situation
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
// Change head->next by it's val (if no val found, will not be changed)
head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);
// Return head or head->next, depending on the val.
// If matched val, return its next, effectively deleting the node.
return (head->val == val) ? head->next : head;
}
};
One pointer from Discussions
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *removeElements(ListNode *head, int val) {
while (head != NULL && head->val == val)
head = head->next;
// He checked NULL here, so he doesn't have to check in while loop
if (head == NULL)
return head;
ListNode *res = head;
while (head->next != NULL) {
if (head->next->val == val)
head->next = head->next->next;
else
head = head->next;
}
return res;
}
};