2.6 KiB
Leetcode Lowest-Common-Ancestor-Of-a-Binary-Search-Tree
2022-07-08 11:53
Algorithms:
#algorithm #binary_search #DFS
Data structures:
#DS #binary_tree #binary_search_tree
Difficulty:
#coding_problems #difficulty_easy
Additional tags:
#leetcode
Revisions:
N/A
Related topics:
Links:
Problem
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Examples
Example 1:
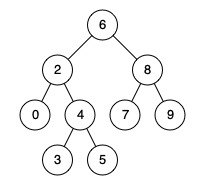
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 Output: 6 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
Example 2:
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 Output: 2 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Input: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1 Output: 2
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 105]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. p != qpandqwill exist in the BST.
Thoughts
[!summary] This is a #binary_search
Because of the features of BST, the maximum val of a left sub-tree is smaller than node, so the valid LCA must meet this:
root->val >= small && root->val <= big
otherwise, search the left or right subtree.
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
// DFS-like recursion
// Base cases
int big = max(q->val, p->val);
int small = min(q->val, p->val);
if (root->val >= small && root->val <= big) {
return root;
} else if (root->val > big) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
} else {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
}
}
};