vault backup: 2022-07-06 13:42:23
This commit is contained in:
parent
b95b655944
commit
7352b7d3a9
111
CS notes/pages/Leetcode Invert-Binary-Tree.md
Normal file
111
CS notes/pages/Leetcode Invert-Binary-Tree.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
|||
# Leetcode Invert-Binary-Tree
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2022-07-06 13:33
|
||||
|
||||
> ##### Algorithms:
|
||||
> #algorithm #DFS #recursion
|
||||
> ##### Data structures:
|
||||
> #DS #binary_tree
|
||||
> ##### Difficulty:
|
||||
> #coding_problem #difficulty-easy
|
||||
> ##### Additional tags:
|
||||
> #leetcode
|
||||
> ##### Revisions:
|
||||
> N/A
|
||||
|
||||
##### Related topics:
|
||||
```expander
|
||||
tag:#recursion tag:#DFS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### Links:
|
||||
- [Link to problem](https://leetcode.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
|
||||
___
|
||||
### Problem
|
||||
|
||||
Given the `root` of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return _its root_.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 1:**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Input:** root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
|
||||
**Output:** [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
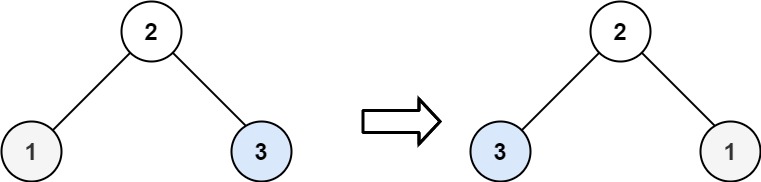
**Input:** root = [2,1,3]
|
||||
**Output:** [2,3,1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 3:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Input:** root = []
|
||||
**Output:** []
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constraints
|
||||
|
||||
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 100]`.
|
||||
- `-100 <= Node.val <= 100`
|
||||
|
||||
### Thoughts
|
||||
|
||||
> [!summary]
|
||||
> This is a #DFS like recursion problem.
|
||||
|
||||
Very simple, think of base cases:
|
||||
- the node is void, skip.
|
||||
And the flow is following
|
||||
|
||||
- Catch base case
|
||||
- Invert sub-trees first
|
||||
- invert left and right node
|
||||
|
||||
### Solution
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* struct TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode *left;
|
||||
* TreeNode *right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
|
||||
* right(right) {}
|
||||
* };
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
void invert(TreeNode *root) {
|
||||
if (!root) {
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
invert(root->left);
|
||||
invert(root->right);
|
||||
|
||||
TreeNode *tmp = root->left;
|
||||
root->left = root->right;
|
||||
root->right = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
TreeNode *invertTree(TreeNode *root) {
|
||||
// Using DFS-like Recursion
|
||||
invert(root);
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in a new issue